Research redefines proteins’ role in the development of spinal sensory cells
A recent study led by Samantha Butler at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA has overturned a common belief about how a certain class of proteins in the spinal cord regulate the formation of nervous system cells—called neurons—during embryonic development. These findings could one day inform the creation of stem cell-based therapies that restore the sense of touch in paralyzed patients.
The study was published in the journal eLife, which was founded in part by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Bone morphogenetic proteins—also known as BMPs—play a key role in human development. These proteins, known as growth factors, are signals that stimulate cellular functions such as growth, proliferation, healing and differentiation. In the developing human spinal cord, BMPs are required for the formation of neurons.
Butler’s study focused on a class of neurons called sensory interneurons. Sensory interneurons allow a person to react to the environment, such as flinching from pain stimulus, feeling comforted by a reassuring squeeze from a loved one or being able to hold a cup of coffee without thinking about it.
The lack of the sense of touch greatly impacts paralyzed patients. For example, people with paralysis often cannot feel the touch of another person and the inability to feel pain could result in burns from inadvertent contact with a hot surface.
“The understanding of sensory interneuron development has lagged far behind that of another class of neurons—called motor neurons—which control the body’s ability to move,” said Butler, associate professor of neurobiology, member of the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center and senior author of the study. “This lack in understanding belies the importance of sensation: it is at the core of human experience. Some patients faced with the reality of paralysis place the recovery of the sense of touch above movement.”
Previous research had suggested that different concentrations of BMPs correlated with the formation of different categories of sensory interneurons. It was thought that a lower concentration of BMPs would result in one category of sensory interneuron, whereas a higher concentration would result in a different category. Butler’s research has found no evidence to support this model.
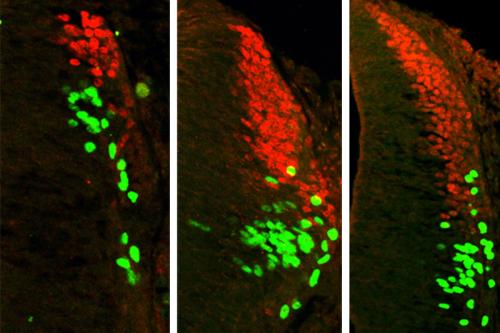
The research team first manipulated the concentration of BMPs in the spinal cord of a chicken embryo. They found that a specific type of BMP always produces specific categories of sensory interneurons, regardless of the concentration of the BMP. The team found that increasing the concentration of a certain type of BMP will make more of the same kinds of sensory interneuron, but will not create a completely different category of sensory interneuron.
The team then applied these findings to mouse embryonic stem cells in lab dishes. They found that by adding specific types of BMPs, they were able to push the stem cells to create two different categories of spinal sensory interneurons. The types of spinal sensory interneurons created control the sensation of the position of body in space—called proprioception—as well as body movements that are activated by touch, such as flinching away from a hot surface.
“Central nervous system injuries and diseases are particularly devastating because the brain and spinal cord are unable to regenerate,” said Madeline Andrews, a predoctoral student in Butler’s lab during the time of this research and first author of the study. “Replacing damaged tissue with sensory interneurons derived from stem cells is a promising therapeutic strategy. Our research, which provides key insights into how sensory interneurons naturally develop, gets us one step closer to that goal.”
Butler’s team now plans to apply their findings to human stem cells as well as drug testing platforms that target diseased sensory interneurons. They also hope to investigate the feasibility of using sensory interneurons in cellular replacement therapies that may one day restore sensation to paralyzed patients.
The research was supported by a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development T32 training grant (HD060549) in developmental biology, stem cells and regeneration, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (RB5-07320) and its Bridges to Research program (TB1-01183), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NS085097) and a UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center-Rose Hills Foundation Training Award.